The Botanicals and Novel Foods Unit (BNV) of the Medicines Evaluation Board agency has two tasks. The first concerns the assessment of herbal, homeopathic and anthroposophic medicines. The MEB takes decisions on market authorisations for these groups of products. As its second task, under the Regulation on Novel Foods, the unit provides policy support to the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (VWS) in connection with the authorisation of novel foods. Since 2018, this has taken place within a European system based on assessments by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport decides on the authorisation for the Netherlands on the basis of this.
The Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) assesses the scientific data of herbal medicines and draws up herbal monographs on the basis of this. Through the Botanicals and Novel Foods Unit, the Netherlands is also represented in the European working group for homeopathic products, the Novel Foods working group in Brussels (which focuses on novel foods) and the working group for herbal products at the European Pharmacopoeia in Strasbourg. In 2020, the Netherlands took on the chairmanship of the HMPC, for a period of three years.
The authorisation procedure for botanicals is the same as for other medicines for human use. A different procedure and other EU laws apply to novel foods. More information about this procedure is available on the MEB website.
Herbals and interactions with medicinal products in the information provision
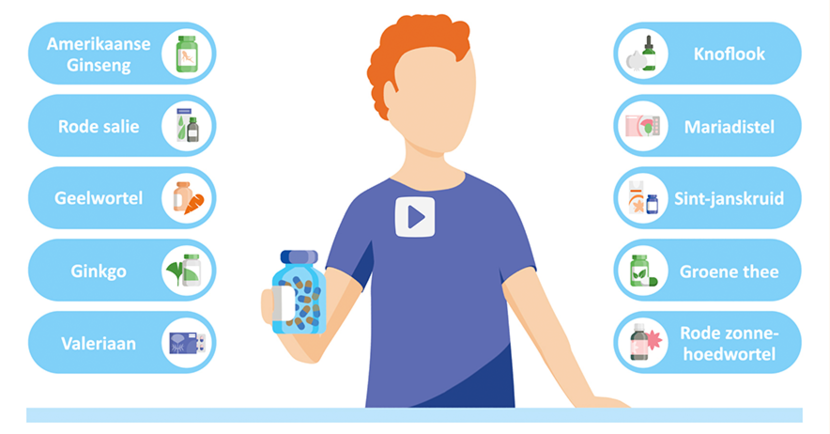
An information campaign to inform the general public about herbals and their interactions with medicines was launched in July 2019. To this end, information about ten herbals was published on the MEB website. The aim of this campaign was to inform patients and healthcare providers about and create awareness of possible risks of combining herbals and medicines. Besides accessible information on the MEB website and an animation video about the interaction with herbals, the MEB also conducted a social media campaign with the help of patient associations. The aim was to expand this information to 10 more herbals in 2020. This will be continued in 2021.

Herbals and homeopathic medicinal products
The number of authorisations for herbals has remained practically unchanged over the years. However, for this time period, a slight decrease is visible for herbals based on a complete dossier and a slight increase for herbals based on traditional use.
Number of market authorisations for herbals
| based on complete dossier | based on traditional use | |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 55 | 50 |
| 2017 | 52 | 54 |
| 2018 | 52 | 53 |
| 2019 | 49 | 55 |
| 2020 | 43 | 55 |
Number of market authorisations for homeopathic medicinal products
In both 2016 and 2018, the number of homeopathic medicines authorised decreased significantly, as many authorisations were withdrawn at the request of companies. The most widely used homeopathic products remain available as authorised homeopathic medicines in various forms of administration. The number of applications in 2020 was virtually the same as in the previous year.
Number of market authorisations for homeopathic medicinal products
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of market authorisations for homeopathic medicinal products | 3073 | 2911 | 2132 | 2130 | 2034 |
Number of concluded cases (including variations)
In 2020, a large number of variations of homeopathic dossiers were concluded, with the data on quality and safety updated for a large number of single homeopathic medicines.
Number of concluded cases
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of concluded cases | 147 | 348 | 203 | 118 | 395 |